【技術(shù)交流】 西北農(nóng)林科技大學(xué)賈漢忠課題組SBB:根際活性氧生成的關(guān)鍵影響因素及其在多環(huán)芳烴轉(zhuǎn)化中的新認(rèn)識(shí)
作者:147小編 更新時(shí)間:2024-10-09 點(diǎn)擊數(shù):
第一作者:劉晉波(西北農(nóng)林科技大學(xué)已畢業(yè)博士生,目前就職于延安大學(xué))
通訊作者:賈漢忠 教授(西北農(nóng)林科技大學(xué))
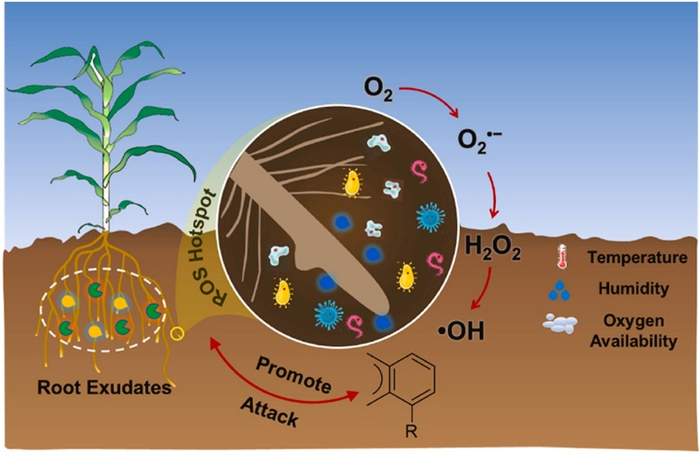
圖文摘要
成果簡(jiǎn)介
近日,賈漢忠教授在Soil Biology and Biochemistry上發(fā)表了題為“Novel insights into the factors influencing rhizosphere reactive oxygen species production and their role in polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons transformation”的研究論文(DOI:10.1016/j.soilbio.2024.109562)。該研究結(jié)合根箱實(shí)驗(yàn)和盆栽實(shí)驗(yàn)系統(tǒng)地闡明了根系發(fā)育和環(huán)境條件對(duì)根際活性氧(ROS)生成的影響以及根際ROS在多環(huán)芳烴(PAHs)轉(zhuǎn)化中的重要作用。
全文速覽
活性氧(ROS)被認(rèn)為是生物地球化學(xué)過程的關(guān)鍵驅(qū)動(dòng)因素。然而,影響根際ROS產(chǎn)生的因素及其在污染物轉(zhuǎn)化中的作用尚不清楚。本研究以玉米作為模式植株,探究了根系發(fā)育過程中根際超氧自由基(O2·-)、雙氧水(H2O2)和羥基自由基(·OH)的時(shí)空變化,并闡明了環(huán)境條件(如環(huán)境溫度,土壤含水量和氧氣有效性)對(duì)ROS產(chǎn)生的影響。原位熒光成像表明,在玉米生長(zhǎng)過程中,ROS逐漸從主根轉(zhuǎn)移到側(cè)根,這表明新發(fā)育的根系是ROS產(chǎn)生的主要貢獻(xiàn)者。三種ROS的含量隨根系生長(zhǎng)而變化,表明根系發(fā)育調(diào)節(jié)ROS的產(chǎn)生。ROS含量在25℃和45%的最大田間持水量條件下達(dá)到最大值,環(huán)境溫度和土壤含水量通過調(diào)節(jié)根系分泌物的釋放,誘導(dǎo)水溶性酚和溶解有機(jī)碳的變化,間接影響ROS的產(chǎn)生。相反,ROS含量隨著氧氣有效性的增加而逐漸增加,其作為前體直接介導(dǎo)ROS的生成。更有趣的是,多環(huán)芳烴(PAHs)的存在顯著增強(qiáng)了ROS的生成,其進(jìn)一步促進(jìn)了PAH的去除,貢獻(xiàn)率為31.4-43.3%。這些發(fā)現(xiàn)為研究根際ROS的產(chǎn)生、分布和環(huán)境效應(yīng)提供了新的見解。
引言
活性氧(ROS),例如超氧自由基(O2·-)、雙氧水(H2O2)和羥基自由基(·OH),普遍存在于各種環(huán)境介質(zhì)中,并有助于碳周轉(zhuǎn)、元素循環(huán)、污染物轉(zhuǎn)化和生物體生理功能的調(diào)節(jié)。然而,影響根際ROS產(chǎn)生的因素及其在污染物轉(zhuǎn)化中的作用目前尚不清楚。因此,本研究通過選取廣泛用于多環(huán)芳烴(PAHs)修復(fù)的植物玉米作為供試植株,用于探究(i)根系發(fā)育過程中ROS(O2·-、H2O2和·OH)的時(shí)空變化;(ii)環(huán)境條件(土壤水分、溫度和氧氣有效性)對(duì)根際ROS生成的影響及其機(jī)制;(iii)根際ROS對(duì)各種PAHs(萘(NAP)、蒽(ANT)和菲(PHE))轉(zhuǎn)化的貢獻(xiàn)。
圖文導(dǎo)讀
根系發(fā)育對(duì)根際ROS生產(chǎn)的影響
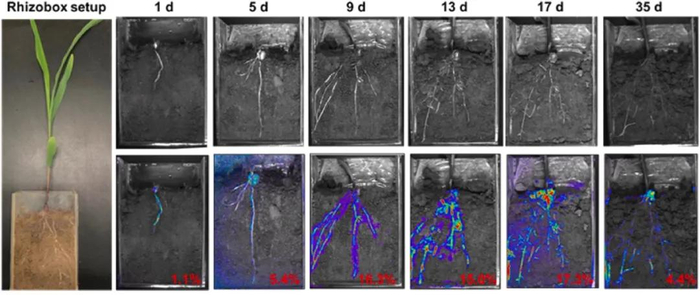
Figure 1. Accumulation of ROS in the rhizosphere of maize. The corresponding fluorescence imaging displayed the hotspot of ROS generation in the root-soil interface at different incubation times, and the red number in the bottom right corner of the picture represented the proportion of ROS hotspots.
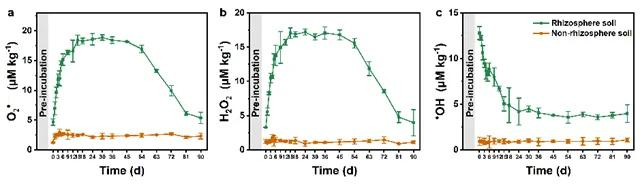
Figure 2. Evolution of contents of O2??(a), H2O2(b), and ?OH(c) in the rhizosphere and non-rhizosphere soils with the growth of maize.The values are presented as the mean ± SD (n = 5), and the error bars represent the standard deviation.
為了探究根系發(fā)育對(duì)根際ROS生成的影響,利用ROS捕獲技術(shù)對(duì)根系發(fā)育過程中ROS的空間演化進(jìn)行了原位表征。結(jié)果表明,在玉米生長(zhǎng)過程中,ROS逐漸從主根轉(zhuǎn)移到側(cè)根,說(shuō)明新發(fā)育的根是ROS產(chǎn)生的主要貢獻(xiàn)者(Figure 1)。為了更深入地了解根際ROS的形成,對(duì)根系發(fā)育過程中三種代表性ROS(O2·-、H2O2和·OH)的含量進(jìn)行了定量化測(cè)定。三種ROS含量隨根系生長(zhǎng)而變化,進(jìn)一步說(shuō)明根系發(fā)育調(diào)節(jié)ROS的產(chǎn)生(Figure 2)。
環(huán)境條件對(duì)根際ROS生產(chǎn)的影響
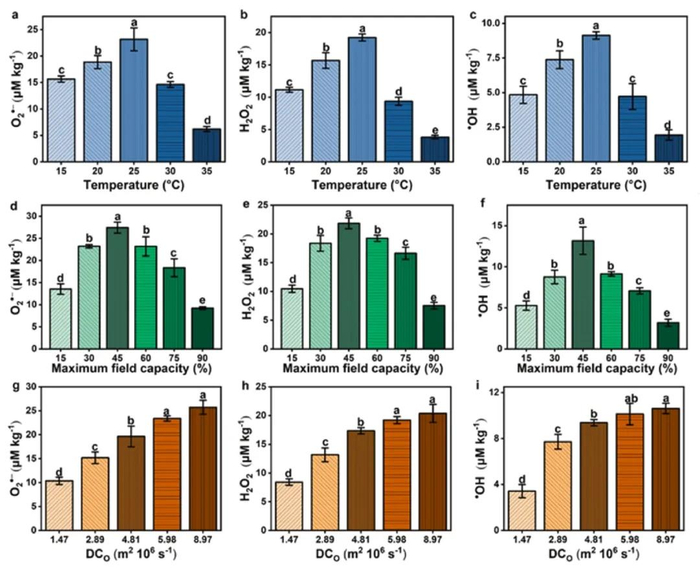
Figure3. Effects of different temperatures on the content of (a) O2·-, (b) H2O2, and (c) ·OH in the rhizosphere of maize; Effects of different humidities on the content of (d) O2·- , (e) H2O2, and (f) ·OH in the rhizosphere of maize; Effects of different oxygen availability on the content of (g) O2·-, (h) H2O2, and (i) ·OH in the rhizosphere of maize. DCo is the diffusivity coefficients of oxygen. The values are presented as the mean ± SD (n = 5), and the error bars represent the standard deviation. Different letters above columns indicate significant differences at p 0.05 level among treatments.
為了探討溫度、土壤含水量和氧氣有效性對(duì)根際ROS生成的影響,通過實(shí)驗(yàn)室模擬不同的環(huán)境條件。結(jié)果發(fā)現(xiàn),ROS含量隨溫度和土壤含水量的增加先增加后降低,而隨氧氣有效性的增加而逐漸增加,分別在25℃和45%的最大田間持水量和8.97 m2 106 s-1條件下達(dá)到最大值,表明環(huán)境條件顯著影響根際ROS的生成(Figure 3)。
環(huán)境條件調(diào)控根際ROS生成的機(jī)制
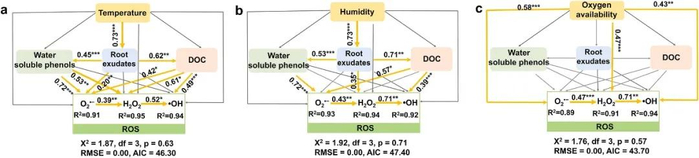
Figure4.The effects of root exudates, water-soluble phenols and DOC on ROS production at different temperatures (a), humidities (b) and oxygen availiablities (c). Single-headed arrows indicate the hypothesized direction of causation. As in other linear models, R2 denotes the proportion of variance explained and appears below every response variable in the model. Model fitness details (χ2, p, RMSE, and AIC) are close to the figure. Orange and blue solid arrows indicate positive and negative correlation, respectively. Grey arrows indicate insignificant correlation (p > 0.05). The arrow width is proportional to the strength of the relationship. The numbers adjacent to the arrows are the standardized path coefficients. *, p 0.05; **, p 0.01; ***, p 0.001.
為了揭示環(huán)境條件調(diào)控根際ROS生成的微觀機(jī)制,對(duì)與ROS生成相關(guān)的因素(如根系分泌物,水溶性酚含量,水溶性有機(jī)碳含量,酶活性以及細(xì)菌群落)進(jìn)行了相關(guān)分析,并對(duì)這些因子調(diào)控ROS生成的路徑進(jìn)行了建模。結(jié)果表明,環(huán)境溫度和土壤含水量通過調(diào)節(jié)根系分泌物的釋放,誘導(dǎo)水溶性酚和溶解有機(jī)碳的變化,間接影響ROS的產(chǎn)生。相反,氧氣有效性則作為前體直接介導(dǎo)ROS的生成(Figure 4)。
PAHs對(duì)根際ROS生成的影響及ROS在PAHs轉(zhuǎn)化中的作用
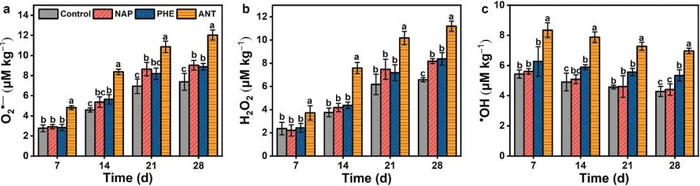
Figure5.The change of (a) O2·-, (b) H2O2, and (c) ·OH in the rhizosphere soil with the growth of maize under the addition of PAHs. The control is the treatment without the addition of PAHs. The NAP, PHE, and ANT are the treatments with the addition of 10 mg kg-1 naphthalene, phenanthrene, and anthracene, respectively. The values are presented as the mean ± SD (n = 5), and the error bars represent the standard deviation. Different letters above columns indicate significant differences at p 0.05 level among treatments.
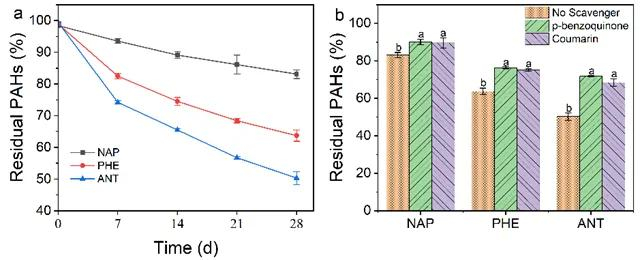
Figure6.(a) Temporalevolutions of various PAHs residual percentage and (b) the effects of quenching agent on PAHs residual percentage in maize rhizosphere.The values are presented as the mean ± SD (n = 5), and the error bars represent the standard deviation. Different letters above columns indicate significant differences at p
為了探究ROS在PAHs轉(zhuǎn)化中的作用,研究了PAHs存在下根際ROS含量的變化及PAHs殘留濃度的變化。結(jié)果表明,PAHs存在促進(jìn)了根際ROS的生成(Figure 5),進(jìn)一步結(jié)合ROS抑制實(shí)驗(yàn)和PAHs殘留濃度的變化說(shuō)明ROS在PAHs轉(zhuǎn)化中具有重要作用,貢獻(xiàn)率為31.4-43.3%(Figure 6)。
小結(jié)
綜上所述,本研究闡明新發(fā)育的根是ROS產(chǎn)生的關(guān)鍵貢獻(xiàn)者。環(huán)境溫度和土壤含水量通過調(diào)節(jié)根分泌物的釋放誘導(dǎo)水溶性酚和水溶性有機(jī)碳的變化間接影響ROS的產(chǎn)生,而氧氣有效性則作為前體直接介導(dǎo)ROS的產(chǎn)生。此外,PAHs的存在增強(qiáng)了ROS的產(chǎn)生,進(jìn)而促進(jìn)了PAHs的轉(zhuǎn)化。這些發(fā)現(xiàn)深化了根系發(fā)育和環(huán)境條件對(duì)根際ROS生成的認(rèn)識(shí),也為ROS介導(dǎo)的PAHs非生物轉(zhuǎn)化提供了新的見解。
作者介紹

賈漢忠 西北農(nóng)林科技大學(xué)教授、博士生導(dǎo)師,入選長(zhǎng)江學(xué)者特聘教授、青年長(zhǎng)江學(xué)者、陜西省特支計(jì)劃-科技創(chuàng)新領(lǐng)軍人才、陜西省杰出青年科學(xué)基金等,獲中國(guó)環(huán)境學(xué)會(huì)青年科學(xué)家獎(jiǎng)(金獎(jiǎng))、中國(guó)農(nóng)學(xué)會(huì)“青年科技獎(jiǎng)”、中國(guó)土壤學(xué)會(huì)“優(yōu)秀青年學(xué)者獎(jiǎng)”等。兼任Environ Chem Lett副主編、Eco-Environ Health期刊編委、B Environ Contam Tox等期刊編委。以第一/通訊作者在GCB、ES&T、SBB等國(guó)內(nèi)外期刊發(fā)表SCI索引論文近200篇,以第一完成人獲得陜西省自然科學(xué)二等獎(jiǎng)、中國(guó)土壤學(xué)會(huì)科學(xué)技術(shù)獎(jiǎng)二等獎(jiǎng)等學(xué)術(shù)成果。長(zhǎng)期從事水土中典型新型污染物的環(huán)境行為與去除技術(shù)、土壤外源碳生物地球化學(xué)過程與效應(yīng)等,特別在環(huán)境自由基的形成過程、環(huán)境行為及生態(tài)效應(yīng)方面開展了深入系統(tǒng)的工作。
電子郵箱: jiahz@nwafu.edu.cn
參考文獻(xiàn):Liu, J.B.; Shen, S.Q.; Zhu, K.C.; Li, Z.Y.; Chen, N.; Lichtfouse, E.; Jia, H.Z., Novel insights into the factors influencing rhizosphere reactive oxygen species production and their role in polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons transformation. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 2024, 198, 109562.
文章鏈接:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2024.109562
(生態(tài)修復(fù)網(wǎng))(轉(zhuǎn)自:生態(tài)修復(fù)網(wǎng))
版權(quán)聲明:本篇文章由朝夕友人官網(wǎng)小編編輯,僅限于學(xué)習(xí)交流,非商業(yè)用途,版權(quán)歸原作者所有,若有來(lái)源標(biāo)注錯(cuò)誤或侵權(quán),請(qǐng)?jiān)诤笈_(tái)留言聯(lián)系小編,將及時(shí)更正、刪除。
上一篇:知名“大空頭”:美聯(lián)儲(chǔ)降息決議對(duì)美股影響有限,還有更重要的因素! 下一篇:選擇回歸的背叛者,還會(huì)再次背叛嗎?受3點(diǎn)因素影響
返回上一層